Share On Social!
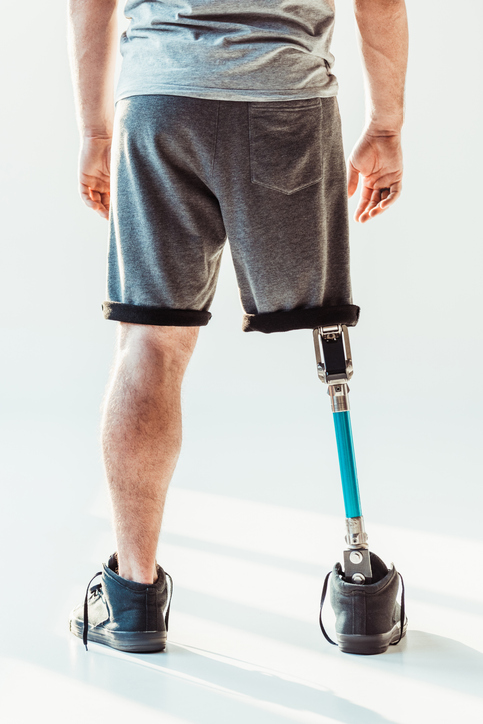
Diabetes development can lead to numerous life-changing complications when the disease spirals out of control, including the amputation of limbs.
As the prevalence of the illness continues to rise––30 million Americans are estimated to have diabetes––black and Latino patients are more likely to have an amputation compared to non-Hispanic whites, CNN reports.
Diabetic foot complications exact a substantial clinical and economic toll in acute care settings, particularly among the rural and working poor.
The Centers for Disease Control reports that in 2014, an estimated 29.1 million adults in the United States, or 9.3% of the adult population, had diabetes.
In California (39.1% Latino), minority groups were more than twice as likely as whites to undergo amputations, according to Kaiser Health News analysis.
The data also showed that Californians with diabetes who live in lower-income neighborhoods have higher rates of lower-extremity amputation than those who reside in more affluent areas.
Amputation is a Major Health Concern

The removal of a lower extremity can have a significant impact on the health and quality of life of the recipient, according to a study in Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
Amputation surgery requires not only additional funds for the rehabilitation process, but also the recipient’s prosthetic limb creation, management, and maintenance.
In emergency department (ED) settings from 2006–2010 in the United States, it is suggested that diabetic foot complications remain common, complex, and costly.
The total national inpatient and ED bill summed to $8.78 billion per year, averaging $115,957 per case for significant amputations.
Amputation is a surgery that requires not only additional funds for the rehabilitation, but also prosthetic creation, management, and maintenance.
Researchers at the University of Texas found high mortality rates among patients after major amputations of a lower limb, secondary to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease.
Patients can also be at high risk for further amputation in the six months after the initial amputation, according to research in Diabetes Care.
Hence, clinicians should focus on preventive efforts and medical resources during individualized at-risk periods for diabetic patients undergoing first-time amputations.
Diabetes among Latinos
Despite national efforts to redress racial/ethnic disparities, Latino Americans continue to share a disproportionate burden of diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
Type 2 diabetes is a major source of morbidity and mortality in the United States, with an estimated prevalence of 9.3%, or more than 29 million people.
Among Latino Americans, the estimated prevalence of diabetes nearly doubles to 16.9%.
The prevalence of diabetes among Hispanic Americans is increasing at a substantially higher rate than non-Hispanic Whites. Moreover, the Latino community is the fastest growing minority group in the U.S.
Eliminating racial/ethnic health disparities will require a substantial reorganization of diabetes care services to ensure access for the most vulnerable communities.
Check out more stories on Diabetes Among Latino and how to get help.
Learn More: Diabetes Among Latinos!
Explore More:
Healthcare AccessBy The Numbers
142
Percent
Expected rise in Latino cancer cases in coming years